
![]()
Phone +420 541 143 246, Fax +420 541 142 224, E-mail: heatlab@fme.vutbr.cz, www.heatlab.cz
Inverse Heat Conduction Task
Unsteady temperature distribution inside test plate is described by differential equation.
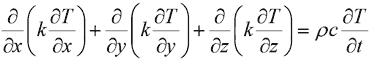
Direct solution of this equation can be done relatively easy using some numerical technique, with knowledge of thermophysical material properties and boundary conditions.
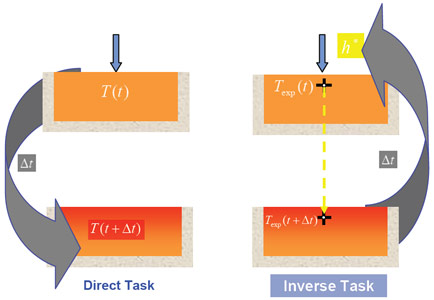
Inverse task means in this case finding of the heat transfer coefficient on the body surface. One or more temperature records at points (sensor positions) inside the body are known from experiment. Method used in this study is based on a minimalization principle. Basic part of this procedure is scheme of heat transfer h computation at time M. An example of this scheme is as shown on Figure.
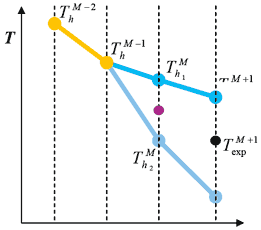
Inverse computation scheme
The direct computation is branched-out at time M-1.Two different values of HTC are applied for a certain number of forward steps r. The HTC h * minimized mean square root deviation between computed ![]() and measured
and measured ![]() temperature.
temperature.
Derivative of this expression is equate to zero 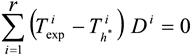
Where 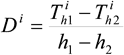 is sensitivity coefficient.
is sensitivity coefficient.
Then the optimal value of HTC h * can be expressed as:
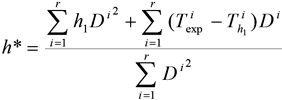
For measurements with fast changes in boundary conditions a new combined inverse method was developed. This method is a mix of Downhill Simplex Optimization Method and Sequential Function Specification Method. Using this combined inverse method more accurate results are obtained and a noise in computed results is greatly suppressed.
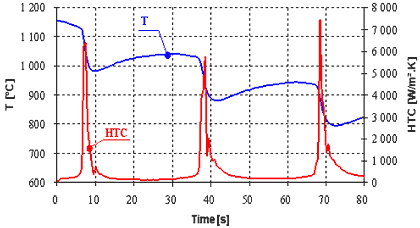
Example of computed heat transfer coefficients ( HTC ) from measured temperature history ( T ) inside a steel plate using Sequential Function Specification Method